How to Get Windscribe Free Trial to Work Again
Clinical trials are enquiry studies that aim to determine whether a medical strategy, handling, or device is safe for utilize or consumption by humans.
These studies may also appraise how effective a medical approach is for specific weather condition or groups of people.
Overall, they add to medical cognition and
To ensure participant safety, trials start with pocket-size groups and examine whether a new method causes any harm or unsatisfactory side furnishings. This is because a technique that is successful in a laboratory or in animals may not be safe or constructive for humans.
The main purpose of clinical trials is research. Trials are designed to add to medical noesis related to the handling, diagnosis, and prevention of diseases or atmospheric condition.

Studies follow strict scientific standards and guidelines that aim to:
- protect participants
- provide reliable and accurate results
Clinical trials on humans occur in the terminal stages of a long, systematic, and thorough inquiry process.
The procedure
Testing on animals enables scientists to encounter how the arroyo affects a living trunk.
Finally, homo testing is carried out in small then larger groups.
Trials may be carried out to:
- Evaluate i or more treatment interventions for a disease, syndrome or condition, such as drugs, medical devices, or approaches to surgery or therapies
- Assess ways to forbid a disease or condition, for example, through medicines, vaccines, and lifestyle changes
- Evaluate ane or more than diagnosis interventions that might identify or diagnose a particular disease or condition
- Examine identification methods for recognizing a condition or risk factors for that condition
- Explore supportive care procedures to better the comfort and quality of life of people with a chronic disease
The outcome of a clinical trial may identify if a new medical strategy, handling or device:
- has a positive effect on patient prognosis
- causes unforeseen impairment
- has no positive benefits or has negative effects
Clinical trials can provide valuable information regarding the cost-effectiveness of a treatment, the clinical value of a diagnostic examination, and how a treatment improves quality of life.
All clinical trials have a primary purpose. These can be broken down into the following categories:
- Treatment: Testing new treatments, new drug combinations, or new approaches to surgery or therapy
- Prevention: Examining ways to improve prevention or recurrence of disease through, for example, medicines, vitamins, vaccines, minerals, and lifestyle changes
- Diagnostic: Finding improved testing techniques and procedures for diagnosing diseases and atmospheric condition
- Screening: Testing the all-time method of identifying certain diseases or health conditions
- Supportive care: Investigating procedures to better comfort and quality of life for patients with a chronic condition
- Health services research: Evaluating the delivery, process, management, organization, or financing of health care
- Bones science: Examining how an intervention works
Clinical trials help ameliorate and advance medical care. The studies provide factual show that tin be used to improve patient care.
Clinical research is only conducted if doctors are unaware of elements such equally:
- whether a new approach works effectively in humans and is safe
- what treatments or strategies piece of work virtually successfully for certain illness and groups of individuals
Various elements are involved in setting upwards, running, and following up a clinical trial.
Clinical trials protocol
A trial follows a comprehensive plan, or protocol. A protocol is the written description of a clinical trial.
It includes the study'south objectives, design and methods, relevant scientific background, and statistical information.
Fundamental information to include may be:
- the number of participants
- who is eligible to have part
- what tests will be given and how oftentimes
- types of data to be collected
- the length of the written report
- detailed data nigh the treatment plan
Avoiding bias
Researchers must have measures to avoid bias.
Bias refers to man choices or other factors that are not related to the protocol but which may affect the results of the trial.
Steps that can help to avert bias are comparison groups, randomization, and masking.
Comparing groups
Near clinical trials apply comparison groups to compare medical strategies and treatments. Results volition show if i group has a improve outcome than the other.
This is normally conducted in one of two ways:
- One grouping receives an existing treatment for a condition, and the second grouping receives a new treatment. Researchers then compare which group has better results.
- One group receives a new treatment, and the 2d group receives a placebo, an inactive product that looks similar the test product.
Randomization
Clinical trials with comparison groups oftentimes use randomization. Participants are allocated to comparison groups by chance rather than by choice. This ways that any differences seen during a trial will be due to the strategy used and non because of pre-existing differences between participants.
Masking or blinding
Masking or blinding helps avoid bias by not informing either the participants or the researchers which handling the participants volition be receiving.
Single bullheaded: This is when either the participants or researchers are unaware, of which group is which.
Double blind: This is when both participants and researchers are unaware.
Misreckoning factors
A confounder tin can misconstrue the true relationship betwixt ii or more characteristics.
For instance, one could conclude that people who carry a cigarette lighter are more than probable to develop lung cancer because carrying a lighter causes lung cancer. Smoking is a confounder in this example.
People who deport a cigarette lighter are more likely to exist smokers, and smokers are more likely to develop lung cancer, but some people may carry a lighter for other purposes.
Non taking this into consideration tin can atomic number 82 to imitation conclusions.
Who is in the enquiry team?
A principle investigator, who is usually a medical doctor, will lead each clinical study.
The research team may include:
- doctors
- nurses
- social workers
- health intendance professionals
- scientists
- data managers
- clinical trial coordinators
Where are clinical trials conducted?
The location volition depend on the blazon of study and who is organizing it.
Some mutual locations include:
- hospitals
- universities
- medical centers
- doctors' offices
- community clinics
- federally-funded and industry-funded research sites
How long do trials last?
This depends on what is being studied, amidst other factors. Some trials last days, while others continue for years.
Before enrolling in a trial, participants will exist told how long it is expected to last.
There are different types of study, and dissimilar ways of organizing them. Here are some written report types.
Observational studies
Cohort studies and instance control studies are examples of observational studies.
Cohort study
A accomplice study is an observational report in which the study population, or cohort, is selected.
Information is gathered to constitute which subjects have either:
- a particular characteristic, such as a blood group that is thought to be related to the development of the disease in question
- exposure to a gene that may exist linked to a disease, for example, cigarette smoking
An individual could be chosen because they smoke. They may then be followed forward in time to see how likely they are to develop a disease, compared with other people.
This type of study is used to study the result of suspected chance factors that cannot be controlled experimentally, such as the impact of smoking on lung cancer.
The principal advantages of cohort studies are:
- Exposure is measured in accelerate of affliction onset and is therefore likely to exist unbiased in terms of disease development.
- Rare exposures can exist investigated by suitable pick of written report cohorts.
- Multiple outcomes — or diseases — can exist studied for whatever one exposure.
- Disease incidence can exist calculated in both the exposed and unexposed groups.
The master disadvantages of cohort studies are:
- They tend to be expensive and fourth dimension-consuming, especially if they are conducted prospectively, which ways moving forward.
- Changes in both exposure status and diagnostic criteria over fourth dimension can affect the classification of individuals co-ordinate to exposure and disease condition.
- There could be information bias in the concluded issue considering the bailiwick's exposure status is known.
- Losses to follow-up may present choice bias.
Case control studies
A case-control study can distinguish risk factors for a particular medical condition.
Researchers compare people with a condition and those without it. Working backward through fourth dimension, they identify how the ii groups differ.
Case-control studies are ever retrospective — looking backward — because they brainstorm with the outcome and and so trace back to investigate exposures.
The
- Findings can exist obtained quickly.
- The study can take place with a minimum of funding or sponsorship.
- They are efficient for investigating rare diseases or diseases with a long induction period.
- A wide range of possible adventure factors can exist examined.
- Multiple exposures tin be studied.
- They crave few study subjects.
The main disadvantages of instance-controlled studies are:
- Incidence information cannot be generated.
- They are field of study to bias.
- It tin can be difficult to obtain authentic, unbiased measures of past exposures if record keeping is inadequate or unreliable. This is called information bias.
- Selection of controls tin can exist problematic. This may innovate selection bias.
- The chronological sequence between exposure and illness may be hard to place.
- They are non appropriate for examining rare exposures, unless the exposure is responsible for a big percentage of cases.
Nested case-control study
In a nested case-command written report, the groups — cases and controls — come from the aforementioned study population, or accomplice.
As the accomplice is followed forwards, the cases that arise become the "cases" in the case-command study. The unaffected participants of the cohort go the "controls."
Nested instance-command studies are less costly and less time-consuming when compared with a cohort study.
Incidence and prevalence rates of the illness can occasionally be projected from a nested instance-control cohort written report. This is not possible from a uncomplicated case-control study, as the total number of exposed individuals and the follow-up times are usually unknown.
The main advantages of nested case-control studies are:
- Efficiency: Not all of the participants of the cohort crave diagnostic testing.
- Flexibility: They allow the testing of hypotheses that were non anticipated when the cohort was planned.
- Reduction of choice bias: Cases and controls are sampled from the same population.
- Reduction of data bias: Risk factor exposure can exist assessed with the investigator blind to case status.
The chief disadvantage is that the results have lower authorisation, due to the small sample size.
Ecological study
An ecological study looks at the relationship betwixt exposure and result of the population or customs.
Mutual categories of ecological study include:
- geographical comparisons
- time-trend assay
- studies of migration
The principal advantages of ecological studies are:
- They are inexpensive, as routinely collected health data tin can exist utilized.
- They are less time-consuming than other studies.
- They are unproblematic and straightforward to empathize.
- The effect of exposures that are measured over groups or areas — such equally diet, air pollution, and temperature — can be investigated.
The primary disadvantages of ecological studies are:
- Errors of deduction known every bit ecological fallacy can occur. It happens when researchers depict conclusions about individuals based solely on the analysis of grouping information.
- Exposure to result relationships is difficult to observe.
- There is a lack of information on confounding factors.
- There may be systematic differences betwixt areas in how exposures are measured.
Experimental studies
Apart from observational studies, there are likewise experimental studies, including handling studies.
Randomized controlled trials
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) randomly allocates individuals either to receive or not receive a particular intervention.
One of two unlike treatments will exist used, or a treatment and a placebo.
This is the near effective study type for identifying which handling works best. Information technology reduces the influence of external variables.
The main advantages of RCTs are:
- There is no conscious or hidden bias on the part of the researcher. This essentially guarantees external validity.
- Misreckoning variables such as age, gender, weight, action level, and then on, can exist canceled out, as long as the sample grouping is big enough.
The main disadvantages of RCTs are:
- They are fourth dimension-consuming.
- They can be expensive.
- They require big sample groups.
- Rare events tin be hard to study.
- Both simulated-positive and false-negative statistical errors are possible.
Adaptive clinical trial
An adaptive pattern method is based on nerveless data. It is both flexible and efficient. Modifications can be made to the trial and the statistical procedures of ongoing clinical trials.
Quasi-experiment
Quasi-experimental, or "nonrandomized" studies, include a broad range of intervention studies that are not randomized. This type of
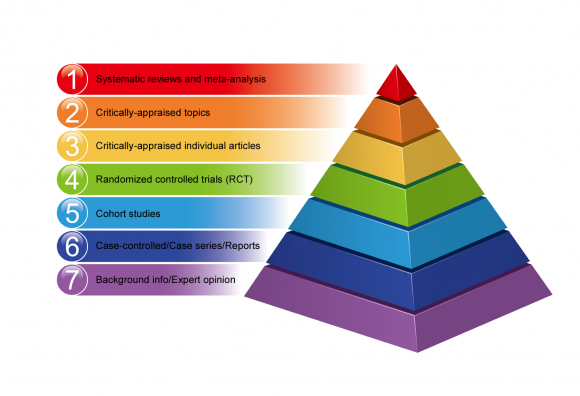
A number of hierarchies of evidence have been founded to enable various research methods to be ranked according to the validity of their findings.
Hierarchies of evidence make it possible to rank various research methods according to the validity of their findings.
Not all enquiry designs are equal in terms of the chance of mistake and bias in their results. Some methods of research provide better bear witness than others.
Below is an example of the hierarchy of evidence-based medicine
Medical research studies are divided into different stages, called phases. For drug testing, these are defined by the FDA.
Early phase trials
Phase 0 trials: Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Phase 0 is an exploratory phase that helps provide clinical information for a new drug at an earlier stage.
- is conducted early in phase 1
- involves very express human exposure
- has no therapeutic or diagnostic intent, beingness limited to screening and microdose studies
Phase 1 trials: Screening for safety
After phase 0, there are four more phases of trials in humans. These frequently overlap. Phases one through iii have place before a license is granted.
Stage one guidelines involve:
- between twenty and eighty salubrious volunteers
- verification of the most frequent side effects of the drug
- finding out how the drug is metabolized and excreted
Phase ii trials: Establishing effectiveness
If stage 1 studies practice not reveal unacceptable toxicity levels, phase 2 studies tin can brainstorm.
This involves:
- between 36 and 300 participants
- collecting preliminary data on whether the drug works in people with a certain disease or condition
- controlled trials to compare those receiving the drug with people in a similar state of affairs who are receiving a dissimilar drug or a placebo
- continued safety evaluation
- studies of brusk-term side effects
Phase 3 trials: Terminal confirmation of condom and effectiveness
If phase 2 has confirmed the effectiveness of a drug, the FDA and sponsors will discuss how to conduct large-scale studies in phase 3.
This will involve:
- between 300 and 3,000 participants
- gathering further information on safety and effectiveness
- studies of different populations
- examining diverse dosages to determine the best prescription amount
- using the drug in combination with other drugs to determine effectiveness
After this phase, the complete information on the new drug is submitted to the wellness authorities.
Review meeting
If the FDA corroborate the product for marketing, post-marketing requirement and commitment studies are conducted.
The FDA
New Drug Awarding
A drug sponsor will complete a New Drug Application (NDA) to ask the FDA to consider approving a new drug for marketing in the U.Southward.
An NDA
- all animal and human information
- analysis of data
- information regarding drug behavior in the torso
- manufacture details
The FDA has threescore days to decide whether to file information technology to be reviewed.
If they make up one's mind to file the NDA, the FDA review team is assigned to evaluate the sponsor's research on the drug's rubber and effectiveness.
The following steps must and so accept place.
Drug labeling: The FDA reviews the drug'southward professional labeling and confirms appropriate information is shared with consumers and health professionals.
Facility inspection: The FDA inspect the facilities where the drug will be manufactured.
Drug approval: FDA reviewers either approve the application or upshot a response letter of the alphabet.
Phase 4 trials: Studies during sales
Phase 4 trials have identify afterward the drug has been canonical for marketing. They are designed to include:
- over 1,000 patients
- comprehensive experience in evaluating the condom and effectiveness of the new medicine in a larger group and subpopulations of patients
- comparison and combination with other available treatments
- evaluation of long-term side effects of the drug
- detection of less common adverse events
- cost-effectiveness of drug therapy compared with other traditional and new therapies
Safe study
Later on the FDA approves a drug, the post-marketing phase begins. The sponsor, usually the manufacturer, submits periodic safe updates to the FDA.
Clinical trials and research tin cost hundreds of millions of dollars. Groups that fund trials may include:
- pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies
- academic medical centers
- voluntary groups and foundations
- National Institutes of Health
- authorities departments
- physicians and health providers
- individuals
The protocol defines who is eligible to participate in a trial.
Possible inclusion criteria may exist:
- having a specific disease or condition
- being "healthy," with no wellness condition
Exclusion criteria are the factors that exclude some people from joining a trial.
Examples include age, gender, a specific type or stage of a disease, previous handling history, and other medical conditions.
Taking part in clinical trials can take
Possible benefits of clinical trials include the post-obit:
- Participants have admission to new treatments.
- If a treatment proves successful, participants will exist among the first to benefit.
- Participants who are not in the grouping receiving a new handling may receive the standard treatment for the particular condition, which may be as good or improve than the new approach.
- Wellness is closely monitored and supported past a squad of wellness providers.
- Information gathered from clinical trials adds to scientific knowledge, may help others, and ultimately improves wellness care.
Possible risks include:
- Standard care for a particular condition can sometimes be better than the new strategy or treatments existence studied.
- The new approach or handling may work well for some participants but not necessarily for others.
- There may exist unexpected or unforeseen side effects, especially in stage 1 and phase two trials and with approaches such every bit gene therapy or new biological treatments.
- Health insurance and wellness providers practice non ever encompass patient care and costs for those participating in clinical trials.
The informed consent certificate explains the risks and potential benefits of taking part in a clinical trial.
Elements that must announced in the document include, among others:
- purpose of inquiry
- foreseeable risks of discomforts
- possible benefits
Participants are expected to
The FDA works to ensure that anyone who is considering joining a trial has access to all the reliable information they need to brand an informed choice, including information about the risks.
While risks to participants are controlled and monitored, some risks may be unavoidable, due to the nature of medical inquiry studies.
Prophylactic of participants is a loftier priority consequence. In every trial, scientific oversight and patient rights contribute to their protection.
Good clinical practise (GCP)
GCP compliance provides the public with confidence that the safety and rights of participants are protected.
It aims to:
- to protect the rights, safety, and welfare of participants
- to guarantee that data collected is reliable, has integrity, and is of an advisable quality
- to provide guidelines and standards for the conduct of clinical inquiry
The foundations of GCP were beginning laid out in 1947. The primary points were that, during any trials, researchers must guarantee:
- voluntary participation
- informed consent
- minimization of gamble
Over time, additions have ranged from establishing additional protection for vulnerable populations to providing guidance to bodies carrying out inquiry.
Patient rights
Ways of protecting patient rights include the following:
Informed consent is the process of supplying clinical trial participants with all of the facts about the trial. It happens before the participants concur to take role and during the course of the trial. Informed consent includes details about the treatments and tests that may be received and the possible benefits and risks.
Other rights: The informed consent document is not a contract; participants may withdraw from the study at any time regardless of whether or non the trial is complete.
Rights and protection for children: A parent or legal guardian must give legal consent if the child is anile 18 years or younger. If a trial may involve a risk that is greater than minimal, both parents must give permission. Children over the age of seven years must agree to be involved in clinical trials.
Information about current clinical trials can be found hither.
Source: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/278779
0 Response to "How to Get Windscribe Free Trial to Work Again"
Post a Comment